
Homepage " Jewelry " engagement rings " diamonds
Every diamond is unique, no two diamonds are the same. Therefore, there are universal standards for the identification of a diamond.
The quality and value of a diamond are defined according to 4 C's: cut, color, clarity and carat.

The cut refers not only to the shape of the diamond, but also to the proportions, symmetry and polish of the diamond.
The diamond cut has 3 primary effects on the appearance of the diamond:
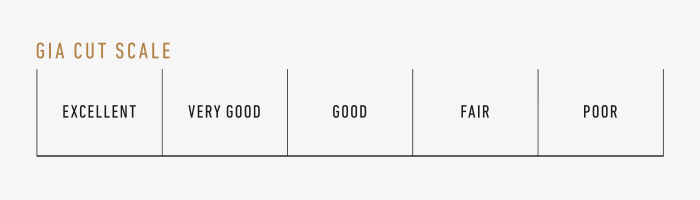
The cut of a diamond is decisive for its beauty. The cut is divided into 5 classes:
Each class is rated according to 5 parameters: excellent, very good, good, medium and low.
If the diamond is not cut well, it will not sparkle as it should. A perfect cut equals more sparkle and fire with an even pattern of light and dark facets.
Diamonds can be cut in several shapes, but the most popular cut is the round cut known as "brilliant". The stone then has 57 facets, which reflect the light to maximum effect and create a radiant brilliance.

The diamond cut also refers to the shape of the diamond.
"Cut " means how well the diamond is cut, while " shape " is the form in which it was cut.
Various forms:
Round / Brilliant
Princess / Prinzess
Cushion / Cushion
Oval / Oval
Emerald
Pear / Peer
Asscher / Asscher
Heart / Herz
Radiant / Radiant
Marquise / Marquise
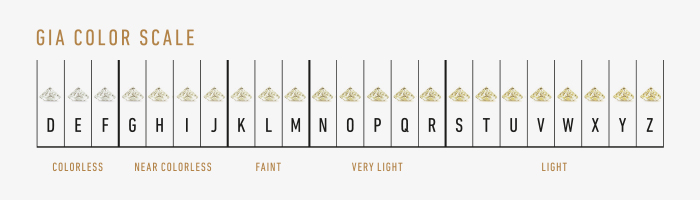
Diamonds can have different colors. They are classified according to international standards, from the whitest, which are considered " colorless" (d) , to a diamond that is slightly yellow (z) . The whitest stones are between the letters D to G.
A perfect diamond has no color at all(D-color, exceptional white +). Diamonds are also available in unusual colors: from brownish to yellow, pink, purple, red, blue and green.
There is also a grading scale for fluorescence, as some diamonds react to UV light, ranging from zero, light, medium to strong.

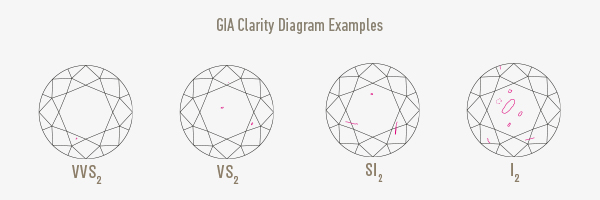
CLARITY / Purity
Diamonds are natural minerals that may have imperfections. Clarity refers to the purity of the diamonds.
The clarity scale reflects the size, number and position of these properties when examined with a 10x loupe. To understand Diamond Clarity, we must first understand how diamonds are created. Natural diamonds are the result of carbon being subjected to tremendous heat and pressure deep within the earth. This process can result in a variety of internal properties known as " inclusions " and external properties known as " blemishes ".
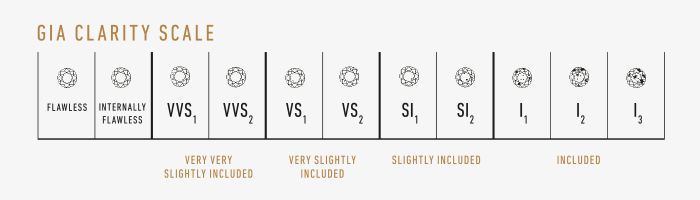
A diamond that has absolutely no flaws is classified as "LC" (flawless) or "FL" (flawless).
Diamonds that have no inclusions visible to the naked eye are of excellent quality. Diamonds with inclusions and difficult to see with a loupe are classified as "VVS" for ("very, very light inclusions") classified. The next classification on the scale is: "VS" ("very small inclusions"). Applies to diamonds that have flaws that can be seen with a magnifying glass, not the naked eye. A diamond is classified as "Si" ("Small Inclusion") when the imperfections are visible to a trained eye. And finally, a diamond is classified as "P" ("Piqué") or "i" (included), when defects are visible to the naked eye.
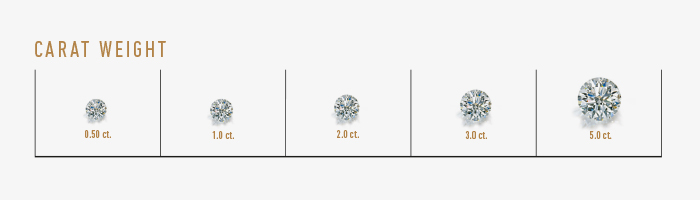
The weight of a diamond is expressed in carats.
One carat corresponds to 0.2 grams or 100 points (equivalent to 200 milligrams).
One carat therefore corresponds to the historical weight of a grain of 0.2 grams. There is another degree of measurement for the smallest stones: the point. This corresponds to 0.01 carat.
A diamond is not only valued by carat alone, but two diamonds with the same carat weight can have very different values depending on their cut, clarity and color.
Diamond certification:
Are you searching
for a specific watch,
which is not on the website?
Cut out the template and stick it onto your stamped parcel.
Alternatively, you can use the standard parcel labels from your parcel service
with the data listed below.
Cut out the template and stick it onto your stamped parcel.
Alternatively, you can use the standard parcel labels from your parcel service
with the data listed below.
Your request has been sent. We will process it as quickly as possible. Enclosed you will receive a copy of your request.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Vimeo. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information